fitting.lagrange¶
-
fitting.lagrange(x, x0, y0)¶ Construct the polynomial over x with the least degree that passes through all points (x0, y0) using Lagrange polynomials.
Parameters: - x (array) – x-values.
- x0 (array) – List of x-coordinates of interpolation points.
- y0 (array) – List of y-coordinates of interpolation points (same shape as x0).
Returns: Lagrange polynomial
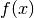 that passes through all data points.
that passes through all data points.Note
The Lagrange form is very susceptible to Runge’s phenomenon, i.e., interpolation divergence; especially when many data points are used.
Example:
# a parabola through three points x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 64) y = lagrange(x, [-3, 0, 3], [1, -3, 6])
